Map of 15-minute cities in Spain Find out your accessibility.
In Spain, more than 60% of the inhabitants have access to essential services within 15 minutes on foot or by bicycle.. Do you want to know if your neighbourhood fulfils the idea of a “15-minute city”? Our comprehensive Deyde DataCentric data analysis shows you.
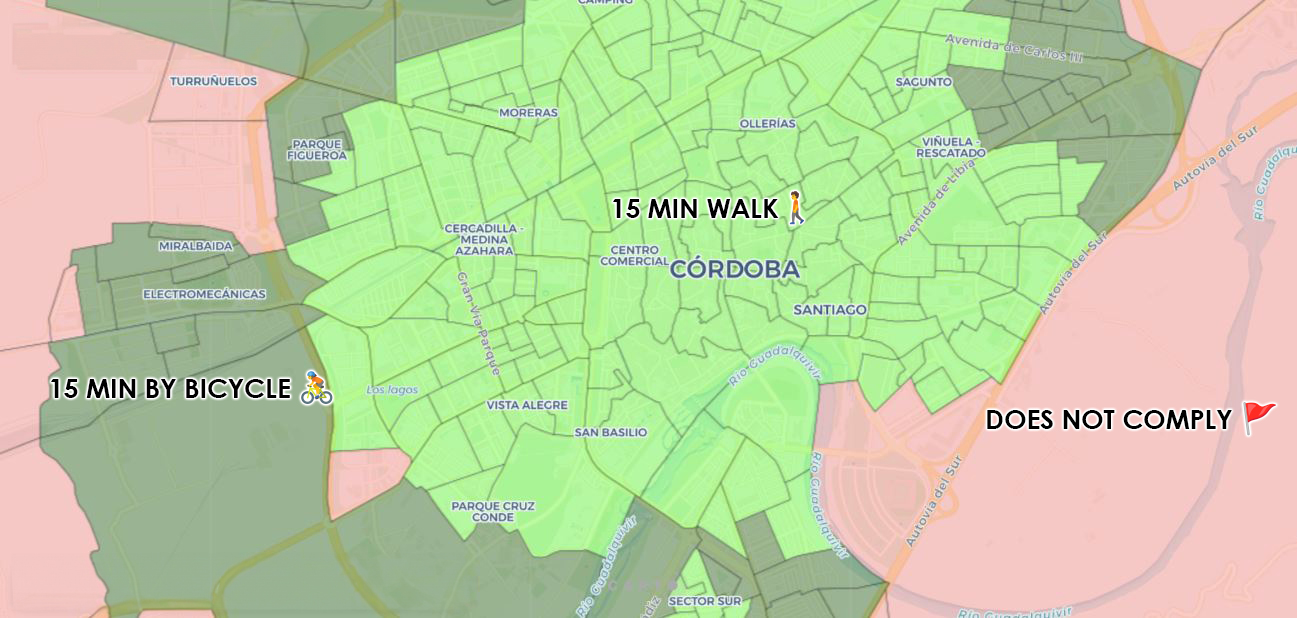
Look on the map to see if your neighbourhood or town meets the 15-minute city.
- Enter an address in the magnifying glass 🔍 at the bottom left of the map.
- You can check an area for compliance with the 6 required categories (default option) or check a specific one. Please do not select more than one category at a time.
- By zooming and clicking on the map you can see detailed information on each census section.
Criteria considered in Deyde DataCentric's data study
Territorial unit: Census section. Distances calculated from the centroid of the census tract:
- Maximum walking distance, 15 min: Radius of 1,200 metres (light green colour).
- Maximum cycling distance, 15 min: Radius of 2,400 metres (dark green colour).
- Non-compliant areas are painted in light reed. If your area is in red it is because it does not comply with one of the 6 categories, activate layer by layer to see which category/s it does not comply with.
6 Categories to be fulfilled, each including a set of basic criteria and endowments (based on Deyde DataCentric business information):
- Supply: Food (supermarkets and shops), banking and service stations.
- Health: Health care (hospitals or health centres) and pharmacies.
- Work: Employability (workforce of located companies/working people) and means of public transport.
- Quality of Life: Green areas and official bodies.
- Leisure: Hospitality (bars, hotels and catering) and entertainment (sports facilities, cinemas and auditoriums).
- Education: Schools and secondary schools.
For more information, read the methodology and check the data source
HIGHLIGHTS:
15-minute cities in Spain
46% of Spain’s population has all services considered basic within a 15-minute walk and 15.1% can reach them in 15 minutes by bicycle. On the other hand, 38.9% do not have all the services studied within 15 minutes either on foot or by bicycle.
The regions with the greatest accessibility to services are Madrid and Catalonia, while those with the least accessibility are Castilla la Mancha and Extremadura.
In terms of proximity in terms of time, the communities of Madrid and Catalonia have the highest percentage of their population living within a 15-minute walkof the services. It is worth noting that only four autonomous communities (Madrid, Catalonia, Aragon and the Basque Country) have more than 50% of their population within a 15-minute walk of all the services analysed.
The categories with most room for improvement areentertainment, work and livingwhile supply, health and education are the most covered service categories.
In large municipalities 96% of the population already lives in a 15-minutes city.
Barcelona is 100% a 15-minute walk city and Bilbao is 100% a 15-minute bike city. In other words, Barcelona and Bilbao, which have their entire population within 15 minutes of all the services analysed, either on foot or by bicycle.
In terms of time, Barcelona, Valencia and Madrid have the highest percentage of their population within a 15-minute walk.
Murcia is one of the larger cities that lags slightly behind its counterparts and has the lowest percentage of population within 15 minutes, with education, entertainment and living being the categories of services that need the most reinforcement.
The municipalities with more than 50,000 inhabitants with the greatest capacity to improve access to services are Molina de Segura (especially in Education and Entertainment), Roquetas de Mar (Work) and Utrera (Entertainment).
What about dormitory towns?
If we analyse the municipalities that form part of the metropolitan area of the top 10 municipalities, we see that 75% of their inhabitants live within a 15-minute walk or bicycle ride of the set of services analysed.
By municipalities, we can see that, in comparison, the municipalities surrounding and adjacent to the city of Barcelona have greater accessibility to all the services analysed than any other large city. In the Top 10 municipalities with the best accessibility, 7 correspond to the Barcelona area, including the city of Barcelona.
The category with the most room for improvement is entertainment and the most covered is supply.
The unfinished business is still the emptied Spain
If we analyse municipalities under 30,000 inhabitants and provinces most affected by depopulation, which fall within the definition of the so-called Empty Spain, we can see large differences in the rural world where 12% of its inhabitants live within 15 minutes walking or cycling distance of all the services analysed. This would leave a population of 4,977,340 inhabitants with the capacity to improve the aspect under study.
Compared to each other, the categories with the most room for improvement are entertainment, living and working.
However, we can highlight that there are 5 municipalities in empty Spain where 100% of the population would live in a 15-minutes city: Béjar, Burela, Jaca, La Seu d’Urgell and Solsona.
Conclusions of the study: Map of 15-minute cities in Spain
The current picture of Spain’s municipalities analysed from the 15-minute city concept shows that 60% of the population already lives in a 15-minute city.
The categories with the most room for improvement are entertainment, work and living, while supply, health and education are the most covered service categories.
Although the development of cities is centralised and it might seem difficult to manage in the big cities, it is true that in the big cities it is possible to access all services for almost the entire population of these municipalities.
The analysis in the so-called dormitory towns characterised in their beginnings by a low neighbourhood fabric, the absence of public spaces and isolation in a car-dependent lifestyle shows that; despite beliefs, 75% of the inhabitants of these municipalities already live in 15-minute cities. Outperforming the national average.
Rural Spain shows the other side of the coin as far as proximity to services is concerned, with only 12% of the municipalities in empty Spain living in a city 15 minutes away.
FAQs - Frequently asked questions about the 15-minute city
What is the 15-minute city?
The 15-minute city is an innovative urban vision that seeks to transform the way we live and travel in urban environments, reducing car dependency and promoting a more sustainable and healthy lifestyle.
A concept that emerged to address the challenge, in urban planning and development, of the growth of megacities (>10 million inhabitants) and promoted in recent years by public bodies to align with the 2030 agenda and the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Conceptually, the 15-minute city should have access to a range of services, considered basic, within 15 minutes by bicycle maximum. This is a radius of 2,400 metres. Within this distance radius, certain services must be accessible, which are usually grouped into 6 categories: Supply, Health, Work, Living, Entertainment and Education.
How many 15-minute cities are there in Spain?
In Spain there are 136 municipalities in which 100% of the population complies with the concept of a 15-minute city and 572 municipalities in which part of the population lives according to this concept. This represents 1.68% and 7.05% of the municipalities in Spain.
Which are the 15-minute cities in Spain?
Some of the cities that comply with the so-called 15-minute city are Barcelona, Bilbao, Pamplona or Santander. The complete list of the 136 municipalities where 100% of the population lives within 15 minutes is as follows:
- Ajangiz
- Alaquàs
- Albal
- Alcorcón
- Aldaia
- Almàssera
- Almussafes
- Ansoáin/Antsoain
- Armilla
- Arrecife
- Badia del Vallès
- Banyoles
- Barañáin/Barañain
- Barberà del Vallès
- Barcelona
- Barrika
- Basauri
- Béjar
- Bellvei
- Benetússer
- Beniparrell
- Benirredrà
- Berango
- Berriozar
- Bilbao
- Bonrepòs i Mirambell
- Bormujos
- Burela
- Burjassot
- Burlada/Burlata
- Cabrera de Mar
- Cabrils
- Cájar
- Caldes d’Estrac
- Calella
- Camas
- Canet de Mar
- Canovelles
- Cardedeu
- Castilleja de Guzmán
- Castilleja de la Cuesta
- Churriana de la Vega
- Cornellà de Llobregat
- Coslada
- Derio
- Eibar
- Eivissa
- Elda
- Esplugues de Llobregat
- Etxebarri
- Figueres
- Forua
- Gernika-Lumo
- Getxo
- Gines
- Godella
- Granollers
- Hospitalet de Llobregat, L’
- Ibarra
- Igualada
- Jaca
- Leaburu
- Leganés
- Leioa
- Lezo
- Llagosta, La
- Llocnou de la Corona
- Malgrat de Mar
- Manlleu
- Martorell
- Masies de Roda, Les
- Masnou, El
- Massamagrell
- Mataró
- Melilla
- Mislata
- Mollet del Vallès
- Montcada i Reixac
- Montgat
- Montmeló
- Montornès del Vallès
- Mont-ras
- Móstoles
- Museros
- Novelda
- Ogíjares
- Olesa de Montserrat
- Ondara
- Ondarroa
- Ortuella
- Pamplona/Iruña
- Parla
- Pineda de Mar
- Pozuelo de Alarcón
- Premià de Dalt
- Premià de Mar
- Puerto de la Cruz
- Pulianas
- Rafelbunyol
- Real de Gandia, el
- Ripollet
- Rocafort
- Sabadell
- Salt
- San Antonio de Benagéber
- San Juan de Aznalfarache
- Sant Adrià de Besòs
- Sant Andreu de la Barca
- Sant Boi de Llobregat
- Sant Feliu de Llobregat
- Sant Joan Despí
- Sant Just Desvern
- Sant Vicenç dels Horts
- Santa Coloma de Gramenet
- Santa Perpètua de Mogoda
- Santander
- Santurtzi
- Sedaví
- Sestao
- Seu d’Urgell, La
- Sobradiel
- Solsona
- Sopela
- Tavernes Blanques
- Teià
- Tolosa
- Tomares
- Tona
- Torremolinos
- Utebo
- Vilablareix
- Vilafranca del Penedès
- Vilassar de Dalt
- Vilassar de Mar
- Villava/Atarrabia
- Xirivella
Where does the data used to create the map come from?
The data is from Deyde DataCentric, which has a database with all active businesses and points of interest in Spain that is a market reference and feeds a large part of the main online business directories. This database is made up of financial sources, websites of more than 500K businesses in Spain, directories and telephone surveys. This makes it the most reputable business information database in the Spanish market. All this information is cleaned, qualified and georeferenced to enrich analytical models and geographic analysis. More information about the data source.